You've heard about blockchain technology. You've seen Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies in the news. But here's what you don't realize: blockchain technology is transforming how we store, verify, and transfer information across the internet—and understanding it is becoming essential.
Blockchain technology might seem complicated, but at its core, it's a simple concept: a digital ledger that's shared, transparent, and incredibly difficult to tamper with. Whether you're curious about cryptocurrencies, interested in how modern systems work, or just want to understand what everyone's talking about, this guide will explain blockchain technology in plain English—no technical background required.
We'll break down what blockchain technology is, how it works, why it matters, and where you might encounter it in everyday life. By the end of this guide, you'll understand blockchain technology well enough to explain it to someone else.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a system for recording information in a way that makes it extremely difficult to change, hack, or cheat the system. Think of it as a digital ledger—like a record book—that's distributed across many computers instead of being stored in one place. These blockchain technologies represent a fundamental shift from centralized to distributed systems.
Here's the simplest way to understand it: imagine a spreadsheet that's duplicated thousands of times across a blockchain network of computers. Every time a new transaction or entry is made, it's added to this spreadsheet. The blockchain network constantly updates and reconciles this spreadsheet, ensuring everyone has the same version. That's essentially what blockchain technology does—it creates a distributed ledger that's synchronized across the entire blockchain network.
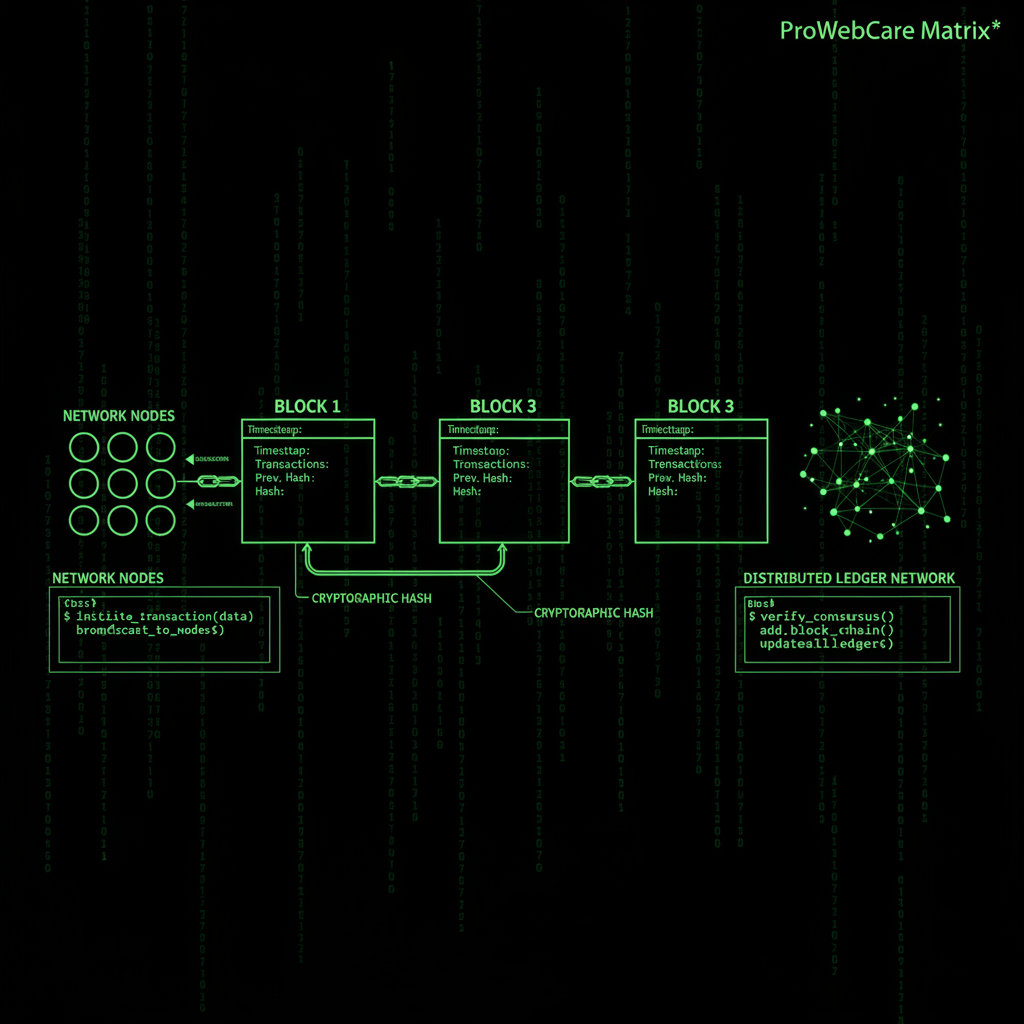
What makes blockchain technology unique is its structure. Information is stored in "blocks," and each block is linked (or "chained") to the previous block using cryptography—a method of secure communication. This creates a chronological chain of blocks, which is where the name "blockchain" comes from. The blockchain network maintains this chain, with each node storing a copy of the blockchain, ensuring redundancy and security.
Key Characteristics of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has several defining features that make these blockchain technologies revolutionary. Understanding these characteristics helps explain why blockchain technology matters and how blockchain networks operate:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases stored in one location, blockchain technology distributes data across many computers (called "nodes") in the blockchain network. This means no single entity controls the entire system. The blockchain network operates through consensus, where multiple nodes must agree on the validity of transactions.
- Transparency: All transactions on a blockchain network are visible to anyone who wants to see them. This creates unprecedented levels of transparency and accountability. When you use blockchain technology, you can verify transactions independently without trusting a central authority.
- Immutability: Once information is recorded on a blockchain, it's extremely difficult to change or delete. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a chain that's nearly impossible to tamper with. This makes blockchain technology ideal for maintaining permanent records.
- Security: Blockchain technology uses advanced cryptography to secure data. To alter a block, you'd need to change it on the majority of computers in the blockchain network simultaneously—which is practically impossible. This security model is one of the key reasons organizations choose to use blockchain technology.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Understanding how blockchain technology works doesn't require a computer science degree. The blockchain network operates through a distributed system where multiple computers (nodes) work together to verify and record transactions. Let's break down how these blockchain technologies function step by step:
Step 1: A Transaction Is Requested
When someone wants to make a transaction—like sending cryptocurrency, recording ownership, or storing data—they request it. In blockchain technology, this transaction includes information like who's involved, what's being transferred, and when it happens.
Step 2: The Transaction Is Broadcast
The transaction request is broadcast to the blockchain network—a network of computers (nodes) running blockchain technology. These nodes in the blockchain network validate the transaction using known algorithms. They check things like: does the sender have enough funds? Is the transaction format correct? Is it a valid request? The blockchain network ensures that all nodes reach consensus about the validity of the transaction before it can be processed.
Step 3: Validation and Verification
Once validated, the transaction is combined with other transactions to create a new block of data. In blockchain technology, these blocks contain multiple transactions, which is more efficient than processing them one at a time.
Step 4: The Block Is Added to the Chain
The new block is added to the existing blockchain network in a way that's permanent and unalterable. This block becomes part of the blockchain, and all nodes in the blockchain network update their copy. Each block contains:
- Data: The actual information (transactions, records, etc.)
- Hash: A unique fingerprint of the block's contents
- Previous Block's Hash: The fingerprint of the previous block, linking them together
- Timestamp: When the block was created
This linking mechanism is what makes blockchain technology secure. If someone tries to alter a block, its hash changes, which breaks the chain because the next block still contains the old hash. The network would immediately recognize this inconsistency and reject the change.
Step 5: The Transaction Is Complete
Once the block is added to the chain, the transaction is complete. It's now part of a permanent, unalterable record that everyone on the network can see. This is one of the core benefits of blockchain technology: creating trust and transparency without needing a central authority.
Types of Blockchain Technologies
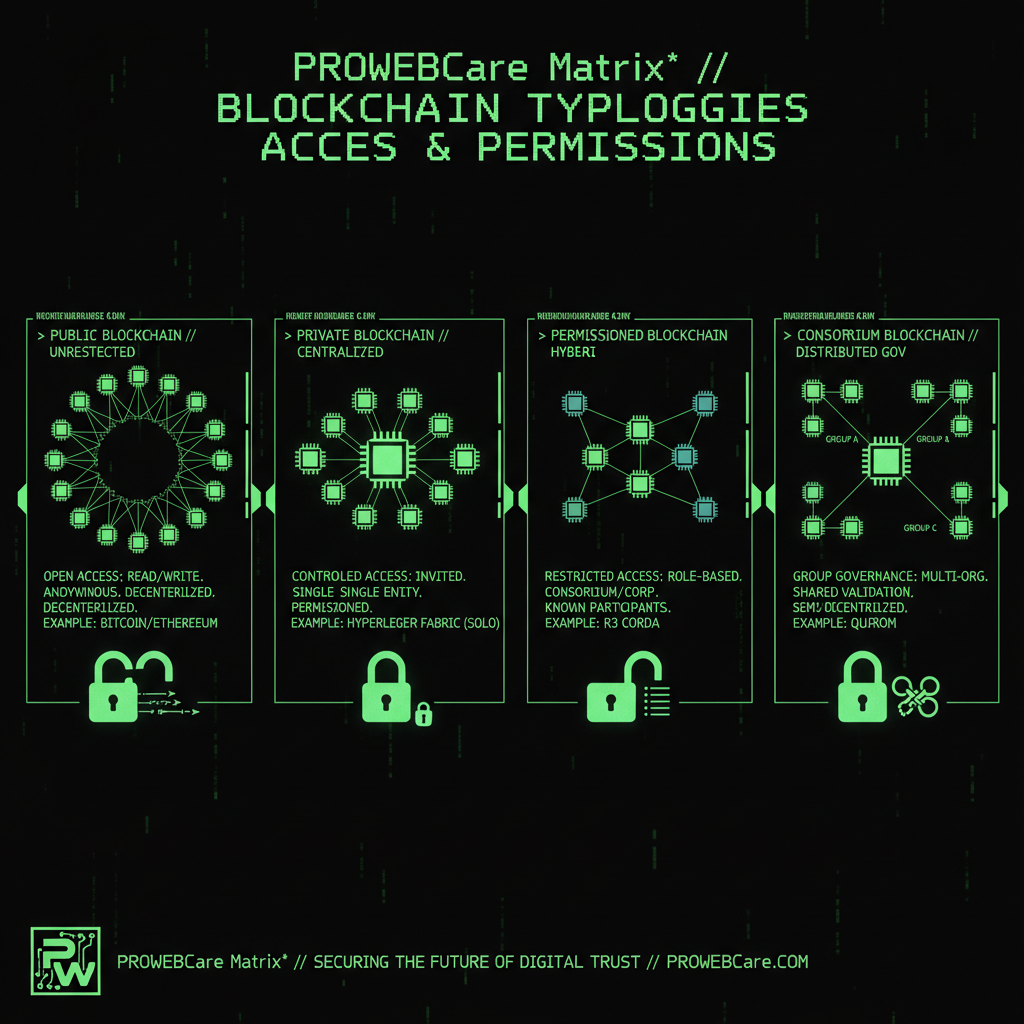
Not all blockchain technologies are the same. Understanding the different types of blockchain helps you choose the right blockchain solution for specific use cases. There are several types of blockchain, each with different characteristics:
Public Blockchain
Public blockchain technologies are open to everyone. Anyone can join the blockchain network, participate in transaction validation, and view the entire blockchain. Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples of public blockchain networks. These blockchain technologies are fully decentralized, transparent, and permissionless. When you use blockchain technology that's public, you're participating in a system where no single entity has control.
Private Blockchain
Private blockchain technologies are restricted to specific organizations or groups. Only authorized participants can join the blockchain network. These blockchain technologies offer more control and privacy but are less decentralized than public blockchains. Companies often use private blockchain technology for internal processes where they need the benefits of blockchain (immutability, security) but want to control access.
Permissioned Blockchain
Permissioned blockchain technologies combine elements of public and private blockchains. Participants need permission to join, but the blockchain network might allow certain levels of public access or transparency. This type of blockchain technology is common in business applications where multiple organizations need to collaborate while maintaining some control over the blockchain network.
Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchain technologies are controlled by a group of organizations rather than a single entity. Multiple organizations share responsibility for maintaining the blockchain network. This type of blockchain technology balances decentralization with efficiency, making it popular for industry-wide applications like supply chain management.
Why Does Blockchain Technology Matter?
Blockchain technology matters because it solves fundamental problems with how we store and transfer information in the digital age. These blockchain technologies address issues of trust, transparency, and efficiency that traditional systems struggle with. Here's why blockchain technology is revolutionary:
Trust Without Intermediaries
Traditionally, when you want to transfer money or verify ownership, you need a trusted third party—like a bank, government agency, or notary. Blockchain technology eliminates the need for these intermediaries by creating a system where trust is built into the technology itself.
For example, if you want to send money internationally, you currently need banks to facilitate the transfer. With blockchain technology, you can send money directly to anyone in the world, 24/7, without bank involvement. The blockchain verifies the transaction automatically.
Security and Transparency
Blockchain technology creates an unprecedented combination of security and transparency. All transactions are visible to everyone (transparency), but they're cryptographically secured (security). This is particularly valuable for industries where trust and verification are critical.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction
By eliminating intermediaries and automating verification, blockchain technology can reduce costs and increase efficiency. Smart contracts—self-executing contracts with terms written into code—can automate complex processes that currently require manual intervention. When you use blockchain technology, you can streamline operations that traditionally require multiple steps and intermediaries. Blockchain technologies enable direct peer-to-peer transactions, reducing processing times and fees associated with traditional systems.
Democratization of Access
Blockchain technology makes it possible for anyone with internet access to participate in financial and digital systems, regardless of their location or access to traditional banking. This has profound implications for financial inclusion worldwide.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain Technology
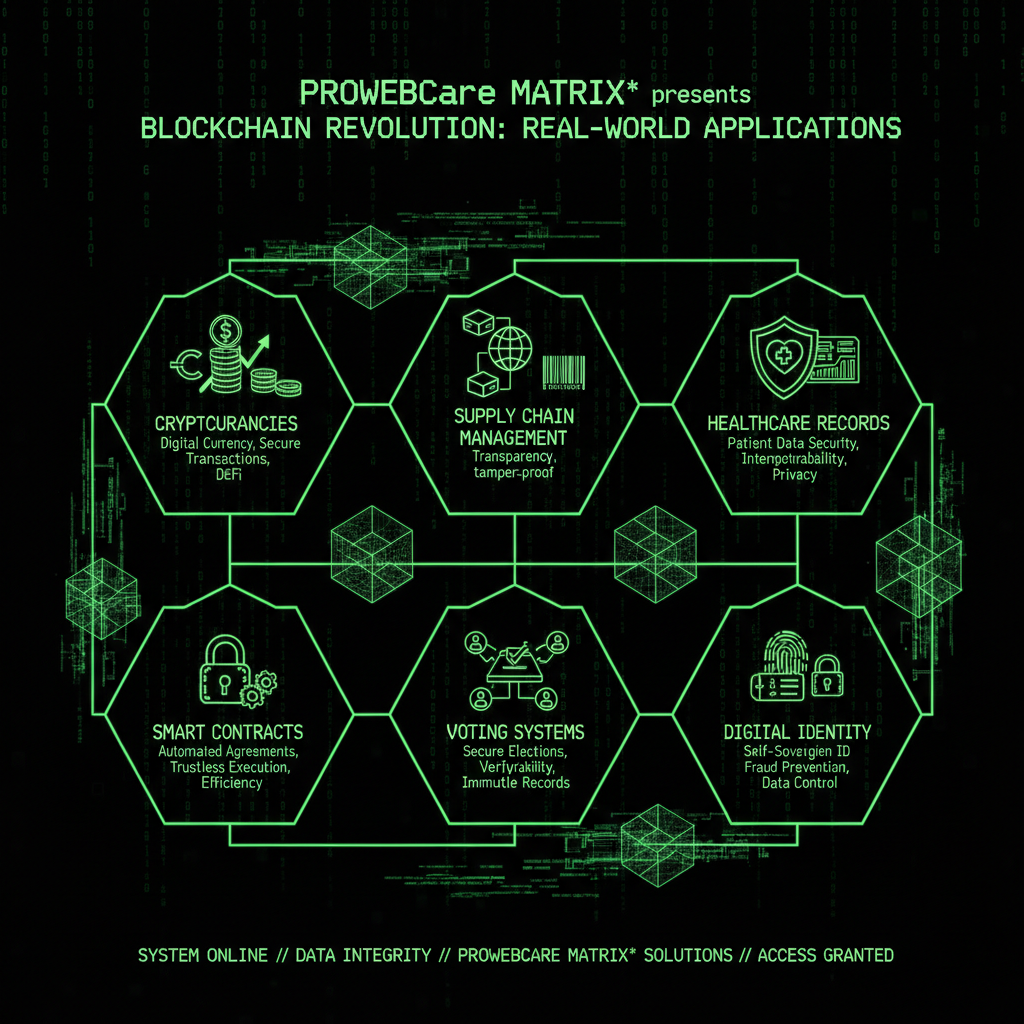
Blockchain technology isn't just theoretical—it's already being used in various industries across the globe. These blockchain technologies are transforming how businesses operate, from financial services to supply chain management. Here are some real-world applications where you can use blockchain technology:
Cryptocurrencies
The most well-known application of blockchain technology is cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These digital currencies use blockchain technology to record transactions and maintain value without a central bank or government. The cryptocurrency and blockchain ecosystem has grown significantly, with thousands of digital assets now using various blockchain technologies. When you use blockchain technology for cryptocurrency transactions, you're participating in a decentralized financial system that operates 24/7 without traditional banking intermediaries.

Supply Chain Management
Companies use blockchain technology to track products from origin to consumer throughout the entire supply chain. For example, you could scan a QR code on a product and see its entire journey through the supply chain, ensuring authenticity and ethical sourcing. Major retailers and manufacturers use blockchain technologies to create transparent, verifiable records of product origins, shipping, and handling. This blockchain application helps prevent fraud, reduce counterfeiting, and ensure products meet quality and ethical standards. The supply chain benefits from blockchain technology because every step is recorded on the blockchain network, creating an immutable audit trail.
Digital Identity
Blockchain technology can create secure, verifiable digital identities that individuals control. This blockchain application could replace traditional ID cards and passports, reducing identity theft and fraud. When you use blockchain technology for digital identity, you maintain control over your personal information while allowing verified access when needed. The blockchain network stores identity credentials in a way that's secure, portable, and tamper-proof.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts use blockchain technology to automatically execute agreements when certain conditions are met. These blockchain technologies eliminate the need for intermediaries in many business processes. For example, a smart contract could automatically release payment to a freelancer when they complete a project, without needing a middleman. When you use blockchain technology with smart contracts, the terms are written into code and stored on the blockchain network, ensuring automatic execution when conditions are met. This blockchain application is revolutionizing industries from insurance to real estate by automating complex agreements.
Voting Systems
Blockchain technology is being explored for voting systems to ensure transparency, prevent fraud, and allow for verifiable results. Each vote would be recorded on the blockchain, making it impossible to alter.
Healthcare Records
Healthcare organizations use blockchain technology to securely store and share patient records. Patients can control who accesses their medical history while ensuring data integrity and privacy.
Real Estate
Blockchain technology can streamline real estate transactions by recording property ownership, reducing paperwork, and making transfers faster and more transparent.
Common Misconceptions About Blockchain Technology
There are several common misconceptions about blockchain technology that can make it seem more complicated or less useful than it actually is. Let's clear them up:
Misconception 1: Blockchain Technology Is Only for Cryptocurrency
While blockchain technology is the foundation of cryptocurrencies, its applications extend far beyond digital currencies. As we've seen, blockchain technology is being used in supply chains, healthcare, voting, identity management, and many other fields.
Misconception 2: Blockchain Technology Is Completely Anonymous
Blockchain technology provides pseudonymity, not complete anonymity. All transactions are visible on the blockchain, but they're linked to addresses (like account numbers) rather than real-world identities. However, these addresses can sometimes be traced back to individuals.
Misconception 3: Blockchain Technology Is Always Decentralized
While many blockchains are decentralized, there are also private or "permissioned" blockchains where only approved participants can join. These still use blockchain technology but operate more like a private network.
Misconception 4: Blockchain Technology Is 100% Secure
While blockchain technology is highly secure, it's not invulnerable. Smart contracts can have bugs, exchanges can be hacked, and users can lose their private keys. The blockchain itself is secure, but the systems built around it can have vulnerabilities.
Misconception 5: Blockchain Technology Is Too Slow
Early blockchain technology implementations were relatively slow, but newer blockchain technology platforms have significantly improved transaction speeds. Some can process thousands of transactions per second, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
How to Get Started with Blockchain Technology
If you're interested in exploring blockchain technology further, here are some practical next steps:
Learn the Basics
Start by understanding the fundamental concepts we've covered in this guide. Blockchain technology has its own terminology—terms like "nodes," "mining," "consensus mechanisms," and "smart contracts"—so familiarizing yourself with these will help you understand more advanced topics.
Experiment with Cryptocurrencies
One of the easiest ways to experience blockchain technology firsthand is through cryptocurrencies. You can create a digital wallet, make a small transaction, and see how blockchain technology works in practice. Remember to start small and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
Explore Blockchain Platforms
Different blockchain platforms serve different purposes. Bitcoin's blockchain focuses on peer-to-peer currency transfers, while Ethereum's blockchain enables smart contracts and decentralized applications. Research different platforms to understand their unique features.
Follow Industry News
Blockchain technology is evolving rapidly. Following industry news, joining online communities, and reading about new developments will help you stay current with how blockchain technology is being used and where it's heading.
Consider Educational Resources
Many online courses, tutorials, and resources are available to deepen your understanding of blockchain technology. From free YouTube tutorials to comprehensive online courses, there are learning options for every level and interest.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is still in its relatively early stages, and its full potential is yet to be realized. Here are some trends and possibilities for the future:
Increased Adoption
As blockchain technology becomes more user-friendly and solves real-world problems, we'll likely see increased adoption across industries. Governments, corporations, and organizations are already exploring blockchain technology for various applications.
Improved Scalability
One of the current challenges with blockchain technology is scalability—the ability to handle large numbers of transactions quickly. Ongoing research and development are focused on improving this, making blockchain technology viable for more applications.
Integration with Other Technologies
Blockchain technology is being combined with artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and other emerging technologies to create innovative solutions. These integrations could unlock new possibilities we haven't even imagined yet.
Regulatory Clarity
As blockchain technology matures, we'll likely see clearer regulations and standards. This could increase confidence and adoption, as well as provide better protection for users.
Environmental Improvements
Early blockchain technology implementations, particularly Bitcoin, were criticized for their high energy consumption. Newer consensus mechanisms and energy-efficient designs are addressing these concerns, making blockchain technology more sustainable.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary way of storing and transferring information that's transparent, secure, and decentralized. At its core, blockchain technology is simple: it's a digital ledger distributed across many computers, creating a system that's difficult to tamper with and doesn't require a central authority.
Understanding blockchain technology is becoming increasingly important as it's adopted across various industries—from finance and supply chains to healthcare and voting systems. Whether you're interested in cryptocurrencies, curious about emerging technologies, or want to understand how modern systems work, grasping the basics of blockchain technology is a valuable skill.
Remember: blockchain technology isn't magic, and it's not perfect. But it represents a fundamental shift in how we think about trust, verification, and digital transactions. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and find new applications, having a solid understanding of its basics will help you navigate an increasingly digital world.
You don't need to be a computer scientist to understand blockchain technology. You just need to grasp the core concepts: distributed ledgers, cryptographic linking, transparency, and decentralization. With these fundamentals, you can understand how blockchain technology works and why it matters—both today and in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system that records information in blocks, which are linked together using cryptography. Each block contains data (like transactions), a unique hash (digital fingerprint), and the hash of the previous block. This creates a chronological chain of blocks that's extremely difficult to tamper with. The blockchain network is distributed across many computers (nodes), making it decentralized and secure. Unlike traditional databases stored in one location, blockchain technology ensures that no single entity controls the entire system, creating trust through technology rather than intermediaries.
What is an example of blockchain technology?
The most famous example of blockchain technology is Bitcoin, which uses a blockchain network to record cryptocurrency transactions. When you send Bitcoin, the transaction is verified by nodes in the blockchain network and added to a block. Once added, it becomes part of the permanent, unalterable record. Another example is supply chain management, where companies use blockchain technology to track products from origin to consumer. For instance, you could scan a QR code on a product and see its entire journey through the supply chain, verifying authenticity. Healthcare organizations also use blockchain technology to securely store and share patient records, giving patients control over their medical data while ensuring data integrity.
What are the 4 types of Blockchain technology?
There are four main types of blockchain technologies based on access and control:
- Public Blockchain: Anyone can join and participate. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum. These blockchain technologies are fully decentralized, transparent, and permissionless.
- Private Blockchain: Restricted to a specific organization or group. Only authorized participants can join. These blockchain technologies offer more control and privacy but are less decentralized.
- Consortium Blockchain: Controlled by a group of organizations rather than a single entity. Multiple organizations share responsibility for maintaining the blockchain network. This type balances decentralization with efficiency.
- Hybrid Blockchain: Combines elements of both public and private blockchain technologies. Some data is public and transparent, while other data remains private and restricted.
Each type of blockchain technology serves different use cases, from public cryptocurrency networks to private supply chain tracking systems.
Where is blockchain used in real life?
Blockchain technology is used in many real-world applications beyond cryptocurrency. In supply chain management, companies use blockchain to track products from origin to consumer, ensuring authenticity and ethical sourcing. Financial institutions use blockchain technology for cross-border payments, reducing costs and processing times. Healthcare organizations use blockchain networks to securely store and share patient records, giving patients control over their medical data. Real estate companies use blockchain technology to streamline property transactions, recording ownership and reducing paperwork. Voting systems are exploring blockchain technology to ensure transparency and prevent fraud. Smart contracts on blockchain platforms automatically execute agreements when conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries in many business processes. These are just some examples of where blockchain technology is being used in real life today.
